Artificial Intelligence: Opportunities, Applications, and Challenges of a Transformative Technology

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most dynamic and promising fields of modern science and technology. No longer a theme confined to science fiction, AI has become a tangible and increasingly integrated component of our everyday lives. From voice assistants and facial recognition systems to self-driving vehicles and AI-powered diagnostic tools, artificial intelligence is now a key driver of technological advancement and resource optimization.
Emerging in the mid-20th century from the ideas of cybernetics pioneers, AI has come a long way—from early experimental algorithms to complex neural networks and deep learning models. This evolution has enabled a transition from solving narrowly defined tasks to building systems capable of autonomous learning, adaptive behavior, and self-improvement without direct human input.
The importance of AI extends far beyond technical innovation. Its impact reaches into economics, social structures, and ethical standards. Understanding how AI works, what it can do, and what risks it poses is essential to harnessing its full potential for humanity’s benefit—while avoiding unintended consequences.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on developing systems that can mimic or reproduce human cognitive functions. These functions include learning, reasoning, pattern recognition, natural language processing, decision-making, and prediction. In essence, AI seeks to enable machines to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence.
Unlike traditional computer programs, which operate based on explicitly defined rules and instructions, AI systems—particularly those built on neural networks—can learn from data. These systems identify patterns and correlations across vast datasets that are often invisible to the human eye. As a result, AI can improve its performance over time, making more accurate predictions and adapting to changing environments.
It is important to distinguish between “narrow AI” and “general AI.” Narrow AI is designed to handle specific tasks—such as speech recognition or playing chess. General AI, still a hypothetical concept, would possess the broad cognitive capabilities of a human being, able to learn and reason across diverse domains with flexibility and autonomy.
In this sense, AI is not merely a software tool but a comprehensive framework of methodologies and algorithms that simulate human intelligence and extend beyond the limits of traditional computing. It represents a foundational technology that is powering scientific, industrial, and social progress at an unprecedented pace.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence Across Sectors
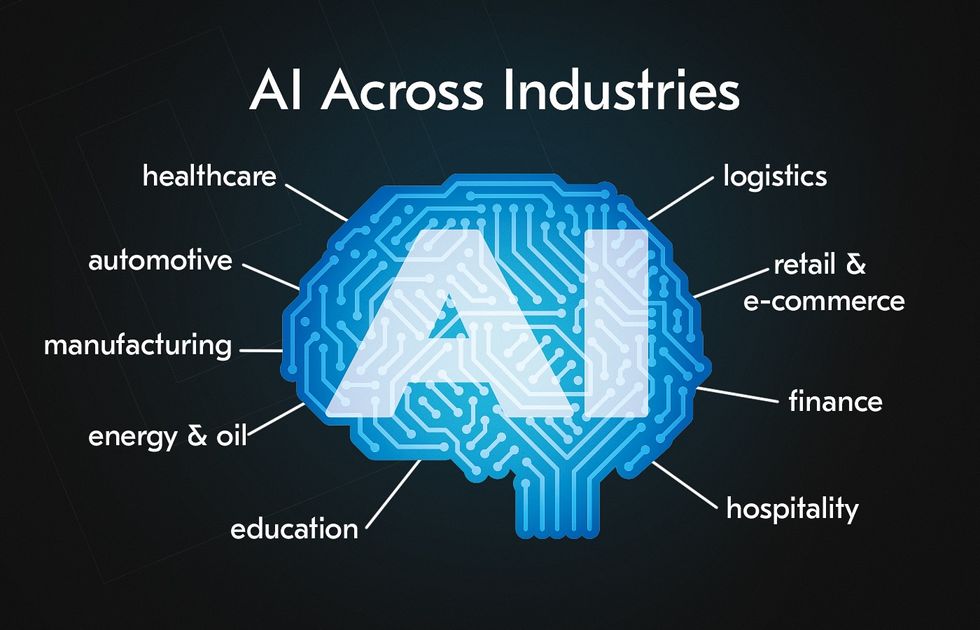
AI is rapidly being deployed across a wide range of industries, offering innovative ways to streamline processes, boost productivity, and enhance service quality. Its ability to learn from and analyze large datasets opens new opportunities for improving virtually every sector.
Industry and Manufacturing
AI enhances industrial efficiency through precise planning, supply chain optimization, and the automation of manual tasks. Vision-equipped robotic systems detect defects in products, while predictive analytics help anticipate equipment failures—reducing downtime and operating costs.
Healthcare
In medicine, AI supports doctors in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs), and detecting abnormalities. It also enables the creation of personalized treatment plans based on patients’ genetic profiles and medical histories. Virtual assistants help monitor patients’ health and provide recommendations, improving the quality and accessibility of care.
Transportation and Logistics
AI powers autonomous vehicles, drones, and intelligent traffic control systems. These applications optimize delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, enhance traffic safety, and make transportation more user-friendly and efficient.
Finance
In banking and insurance, AI is used to assess credit risk, detect fraud, forecast market trends, and automate financial advisory services. AI-driven chatbots deliver instant customer support, improving responsiveness and user satisfaction.
Education
AI-powered platforms tailor educational content to individual learners, suggesting optimal learning paths and providing intelligent assessment tools. This personalizes and enhances the learning experience, helping students achieve better outcomes.
Marketing and Customer Service
By analyzing user behavior, AI enables businesses to better understand their target audiences and deliver personalized product and service recommendations. Chatbots and virtual assistants facilitate real-time, round-the-clock communication, improving customer loyalty and service quality.
AI is becoming a core component of every major economic and social domain, helping streamline decision-making, increase access to services, and drive technological innovation.
Benefits and Advantages of AI
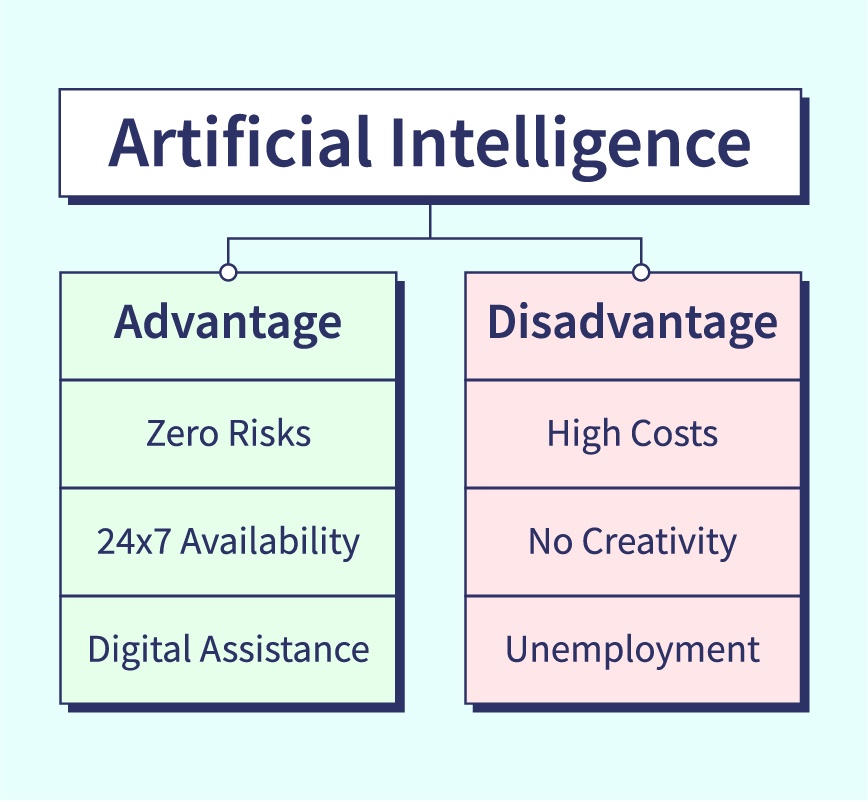
AI offers a unique set of benefits that support more efficient resource use, better decision-making, and faster progress in science and industry. Its adaptability and learning capabilities make it a powerful tool for professionals and organizations around the world.
Efficiency and Productivity Gains
AI algorithms process massive volumes of data rapidly and accurately. This enables real-time decision-making, reduces error rates, optimizes costs, and accelerates production cycles.
Self-Learning and Adaptability
AI systems improve continuously by learning from new data and adapting to changing conditions. This allows organizations to respond swiftly to unexpected challenges and develop creative solutions.
Reduction of Human Error
Unlike humans, AI systems don’t suffer from fatigue or emotion-driven mistakes. By strictly following defined protocols, they enhance the accuracy and reliability of critical operations.
Optimized Resource Management
AI supports smarter use of time, energy, materials, and capital. In logistics, for instance, it helps plan optimal delivery routes, while in manufacturing, it enables more efficient use of raw materials and reduces waste.
Catalyst for Innovation

AI’s ability to detect patterns and correlations fuels breakthroughs in fields like medicine, environmental science, energy, and space exploration. It can uncover hidden insights and guide the development of next-generation technologies.
AI is not just a tool for efficiency—it’s a foundation for a smarter, safer, and more sustainable future.
Ethical and Societal Challenges
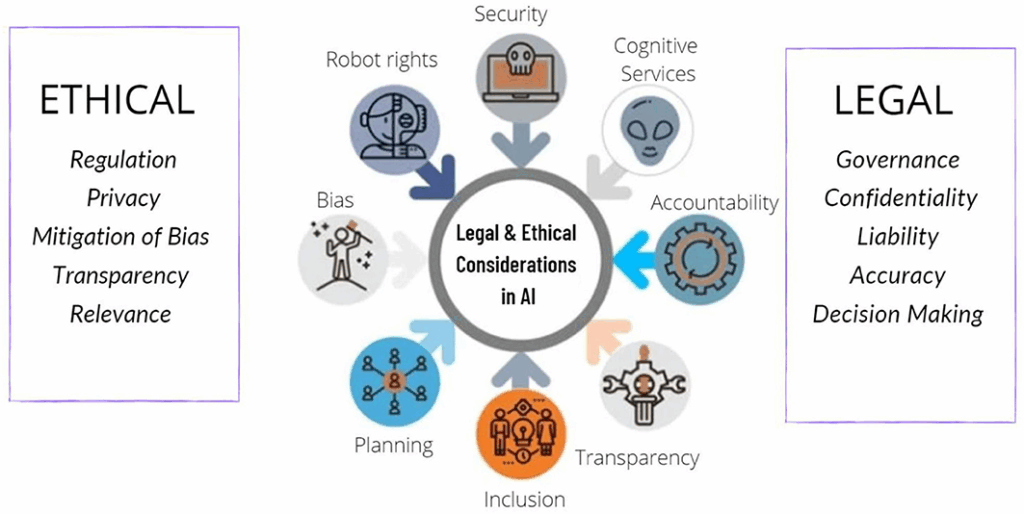
Despite its benefits, AI poses complex ethical and societal questions. If left unaddressed, these issues could lead to unintended harms, including privacy violations, algorithmic bias, growing inequality, and loss of human oversight. Building a responsible AI future requires a collective effort from governments, developers, and civil society.
Privacy and Data Protection
AI systems rely on large volumes of personal data. Without strong regulatory frameworks, there is a risk of unauthorized data access, surveillance, and misuse of personal information for commercial or political purposes.
Bias and Discrimination
AI models often reflect the biases present in the data they are trained on. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes in areas like hiring, lending, or law enforcement. Transparency, fairness, and algorithmic auditing are necessary to prevent such outcomes.
Job Displacement and Economic Inequality
Automation may reduce demand for certain job types, especially those involving routine tasks. This requires re-skilling initiatives, updated education systems, and policies to ensure equitable distribution of AI’s benefits.
The “Black Box” Problem
Many AI systems operate in ways that are not transparent or explainable. When decisions are made by opaque algorithms, trust and accountability suffer. Developing explainable AI models is essential to ensuring oversight and public confidence.
Global Regulation and Cooperation
The fast pace of AI innovation demands international legal frameworks to govern its ethical use. Collaboration among states, businesses, academia, and civil organizations is crucial for establishing balanced policies and preventing misuse.
Ethical AI development depends on transparency, accountability, public awareness, and inclusive policymaking to guide technological advancement in socially responsible directions.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
AI is evolving rapidly, and its influence is only expected to grow. With its capacity for automation, data analysis, and self-improvement, AI is set to revolutionize how we work, live, and interact with technology.
Toward General AI and the Transformation of Work
While current systems mostly perform narrow tasks, the long-term goal is the development of general AI capable of human-like reasoning and learning. This would transform the nature of work—automating routine tasks while enabling humans to focus on creative, emotional, and strategic roles.
Human-AI Collaboration
The future of AI involves not only autonomous systems but also hybrid models that combine human intuition with machine intelligence. These partnerships will enhance decision-making and help build systems that reflect human values and ethical reasoning.
Breakthroughs Across Industries
AI will drive new discoveries in healthcare, agriculture, energy, and beyond. In medicine, AI will help decode the human genome and personalize treatments. In farming, it will support precision agriculture and sustainability. In energy, it will optimize electricity distribution and reduce environmental impact.
Education for the AI Era

Preparing the workforce of the future will require updated curricula that teach people how to work with AI, interpret its outputs, and supervise intelligent systems. Critical thinking, digital literacy, and ethical awareness will be essential skills.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not just another wave of technological progress—it is a foundational shift in how societies operate, how knowledge is created, and how decisions are made. Its transformative potential is immense, but so are the risks if mismanaged. Balancing innovation with ethical responsibility will be crucial to building a future where AI serves all of humanity equitably and transparently.













Comments are closed